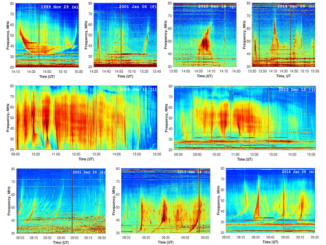
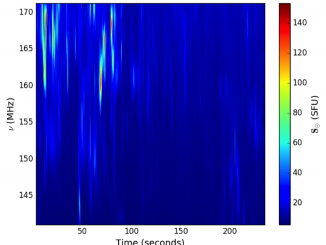
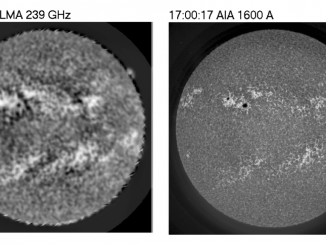
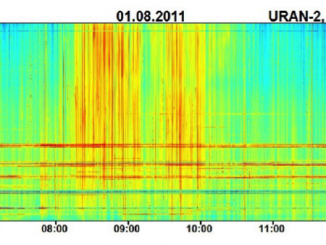
Traveling Ionospheric Disturbances as Huge Natural Lenses: Solar Radio Emission Focusing Effect
by A. Koval et al*
The solar radio emission in meter-decameter wavelengths demonstrates a plentiful variety of solar radio bursts of different types (with branching to sub-types) as well as events not belonging to any specific type (Melnik et al. 2005). The last group includes variable solar emissions that result from radiation processes affected by propagation effects in the terrestrial ionosphere. Particularly, low-frequency solar radiation passing through the ionosphere could be subject to different influences […]