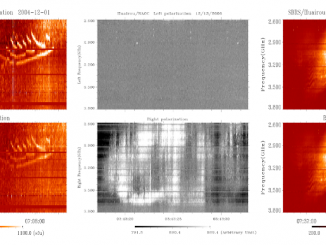
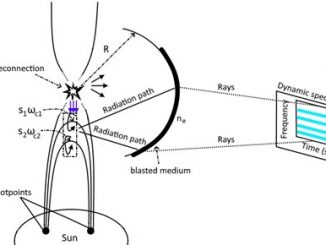
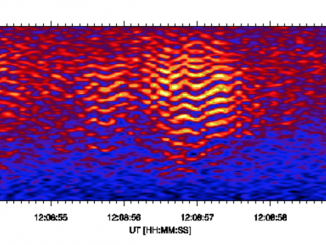
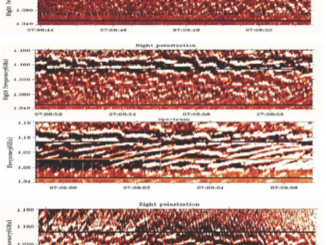
The physics of solar spectral imaging observations in dm-cm wavelengths and space weather by Tan et al.
Recent years, several new generation solar radio telescopes operating in the centimeter decimeter (dm-cm) wavelengths have emerged in the world, including the Mingantu Spectral Radioheliograph (MUSER, 0.4-15GHz) (Yan et al. 2021), the Expanded Owens Valley Solar Array (EOVSA, 1-18GHz) (Gary et al. 2018), and the Siberian Radio Heliograph (SRH, 3-24GHz) (Altyntsev et al. 2020). Due to the fact that the solar radio emission in dm-cm wavelengths mainly originates from the […]