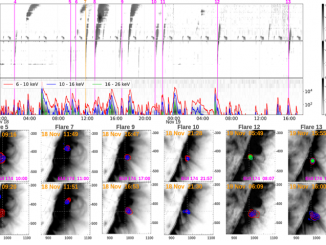
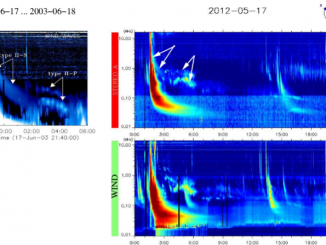
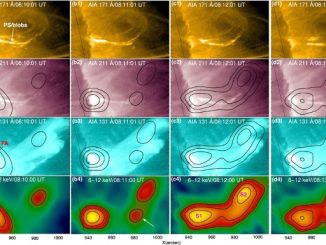
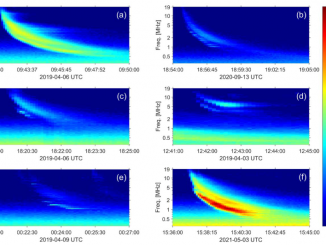
Connecting energetic electrons at the Sun and in the heliosphere through X-ray and radio diagnostics by D. Paipa-Leon et al.
Solar flares accelerate energetic electrons. While some of them escape into interplanetary space and produce interplanetary Type III solar radio bursts, the electrons interacting with the solar atmosphere produce Hard X-ray emission (HXR). Many studies relating the observations of type III radio bursts and HXR emissions have been performed since the first observations of their temporal association (e.g., Kane 1972, 1981). More recently, statistical studies were done by https://www.aanda.org/articles/aa/full_html/2025/02/aa52278-24/aa52278-24.html and James & Vilmer (2023) […]