High School Students Nationwide Help Monitor Solar Activities with Radio Antennas by M. Akhavan-Tafti et al.
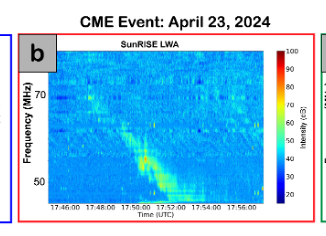
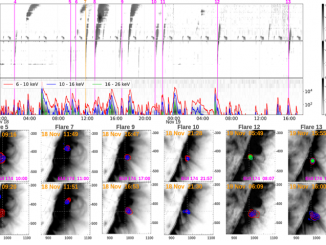
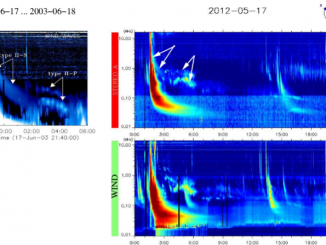
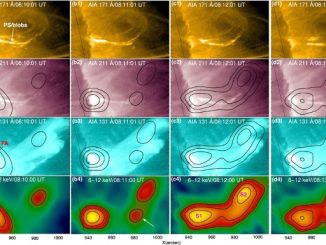
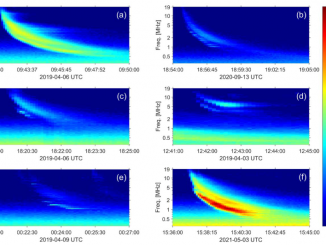
It may surprise you to learn that when the Sun has an outburst, such as a solar flare or a giant eruption of charged gas called a coronal mass ejection (CME), it threatens the health and safety of astronauts or satellites in space. These events also send out invisible shock waves that can disrupt power grids and communications here on Earth. These shock waves produce special radio signals that can […]