Multi-Loop Structure of Nonthermal Microwave Sources in a Major Long-Duration Flare
by V. Grechnev et al.*
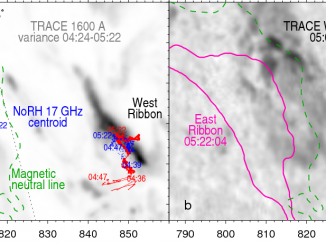
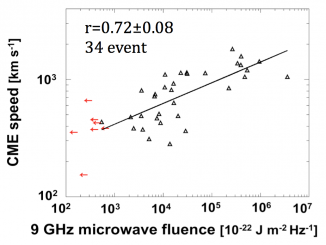
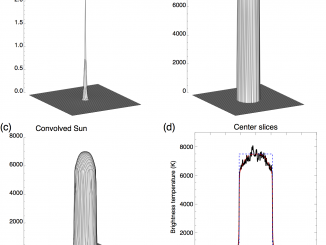
Hard X-ray (HXR) and microwave observations of flares show only a few nonthermal sources. They are simple and compact, especially in impulsive flares, suggesting involvement of one to two loops. Hanaoka (1996) and Nishio et al. (1997) interpreted these observations in terms of double-loop flares. This view was later extended up to long-duration flares (Tzatzakis, Nindos, and Alissandrakis, 2008). A concept of a simple flare loop became dominant. However, observations […]