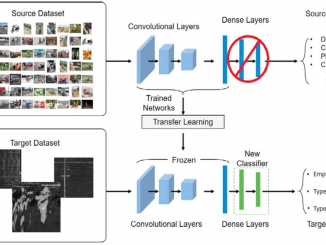
Classification of Type II and Type III Solar Radio Bursts Using Transfer Learning by H. le Roux et al.
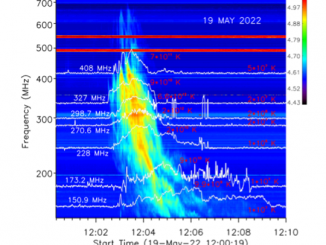
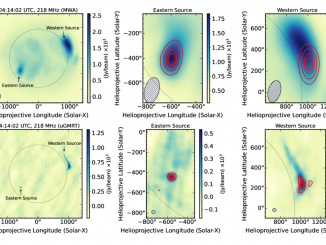
Solar radio bursts (SRBs) are some of the most interesting signatures of solar activity. Their correlation with large solar eruptions and well-documented disruption to technological infrastructure especially highlights their relevance (Temmer 2021; Li et al. 2024; Liang et al. 2024). As the volume of radio data grows, it becomes increasingly important to ensure that there are reliable automated methods for the classification of SRBs, especially if these methods can contribute […]