3D reconstruction of CME-driven shock-streamer interaction as a coronal magnetic field diagnostics
by S. Mancuso et al.*
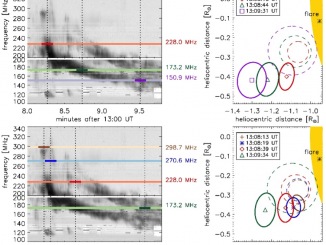
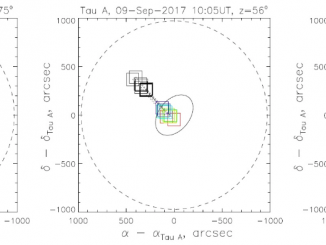
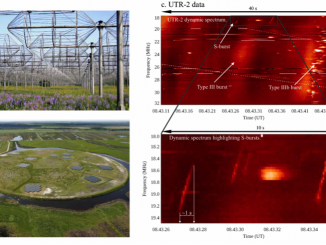
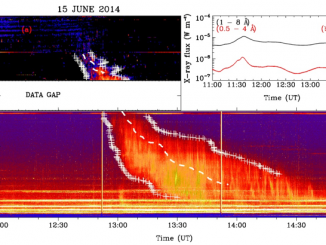
Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs) expelled from the Sun can drive shocks that accelerate electrons which, in turn, produce electrostatic oscillations called Langmuir waves. These waves are then converted into escaping e.m. radiation, known as type II solar radio bursts, emitted near the fundamental and/or harmonic of the local electron plasma frequency. As shocks propagate outward from the Sun to regions of lower plasma density, type IIs appear in dynamic spectra […]