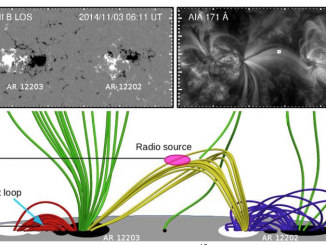
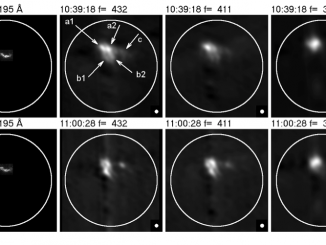
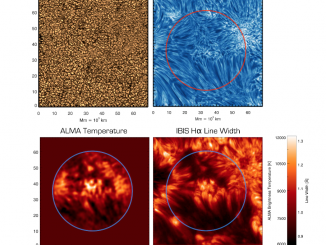
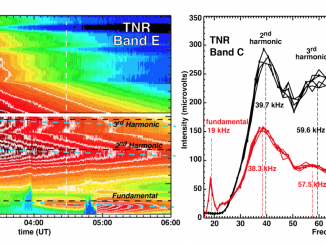
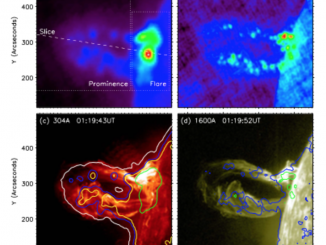
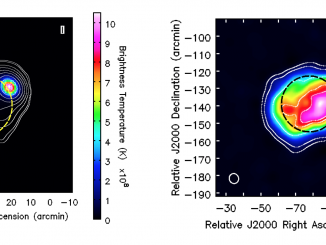
A microflare associated with periodic particle acceleration
by A. Mohan et al.*
Microflares are weaker cousins of large flares with 103 to 106 times less energies. They are also much more ubiquitous and frequent than larger flares. A very common phenomena of the Extreme Ultra-Violet (EUV) corona, namely the Active Region Transient Brightening (ARTB; Shimizu, 1996) event is known to be associated with microflares. The ARTBs are associated with active coronal loops of length ranging from 5 – 40 Mm and often […]