Spectral Structures of Type II Solar Radio Bursts and Solar Energetic Particles
by K. Iwai
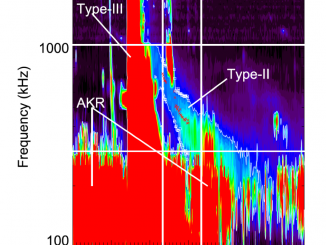
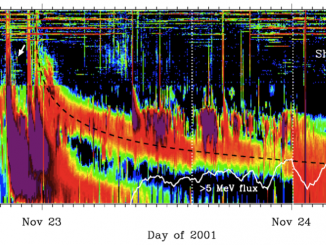
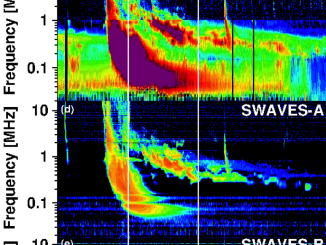
Solar eruptive phenomena, such as flares and coronal mass ejections (CMEs), generate high-energy particles called solar energetic particles (SEPs). Severe SEP events sometimes cause satellite anomalies and radiation exposure to humans in space. Hence, understanding and forecasting SEPs is an important issue in space weather. Type II solar radio bursts are nonthermal radio emissions with negative frequency drift observed between the metric and kilometric frequency range. They are thought to […]