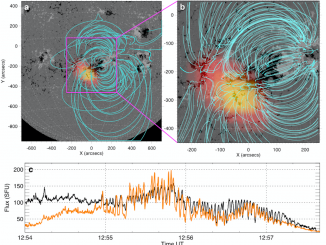
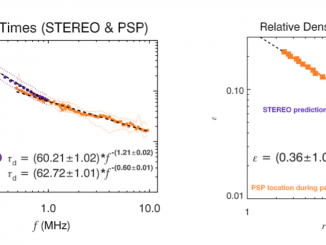
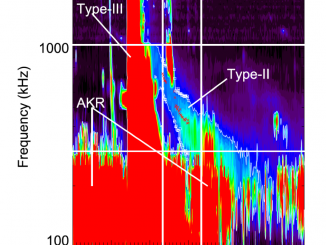
Loss-cone instability modulation due to a magnetohydrodynamic sausage mode oscillation in the solar corona
by E. P. Carley et al.*
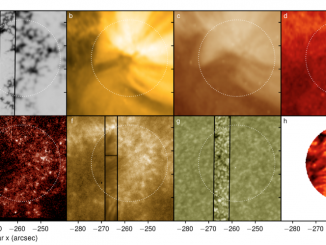
Flare accelerated electrons emit light from X-rays to radio waves, which sometimes show highly regular and periodic intensity pulsations (Nakariakov et al. 2009). However, the processes that bring about these pulsations remains a hotly debated topic. The primary candidates are periodic magnetic reconnection, magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) oscillations, or some complex combination of both (Aschwanden et al. 1986, Nakariakov et al. 2006). Plasma dynamics of these processes can play out on timescales […]