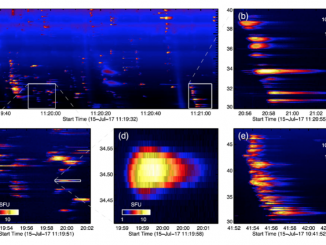
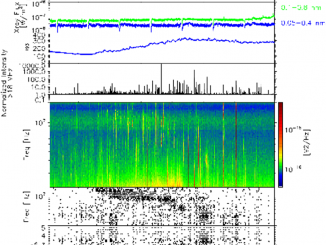
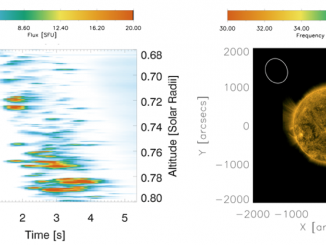
LOFAR size and shape measurements of solar metric radio burst sources
by Gordovskyy et al
The plasma density and magnetic field in the upper solar corona and inner heliosphere are not sufficient to produce detectable bremsstrahlung hard X-ray or gyrosynchrotron microwave emissions, making metric and decametric coherent radio emissions the only tool for probing energetic electrons in these layers of the solar atmosphere (e.g. McLean & Labrum 1985; Pick & Vilmer 2008 as reviews). This source of information is vital to understanding the underlying mechanisms […]