Solar chromospheric temperature diagnostics: A joint Hα – ALMA analysis
by K. Reardon et al
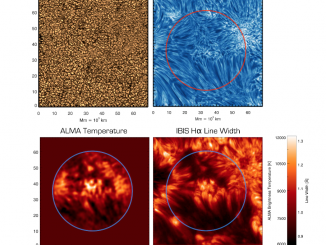
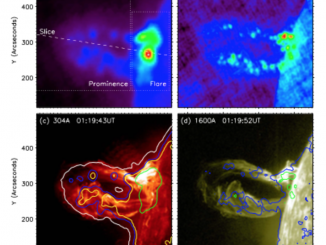
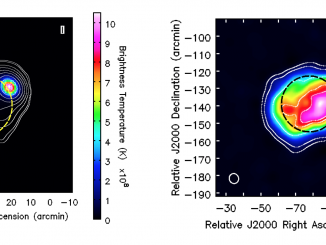
There are many challenges in inferring the spatially and temporally varying temperatures of the dynamic solar chromosphere. The principal problem has been the complex formation of the spectral lines in the UV, visible, and infrared that have been the prime diagnostics to probe this region of the atmosphere. The Atacama Large Millimeter Array (ALMA), which became available for solar observations in 2016, promises to help address this issue by observing […]